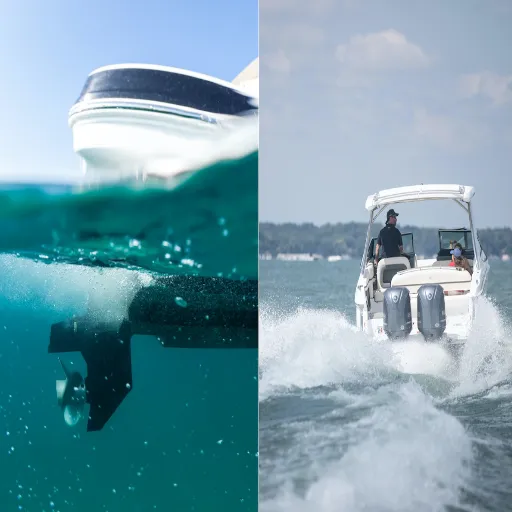
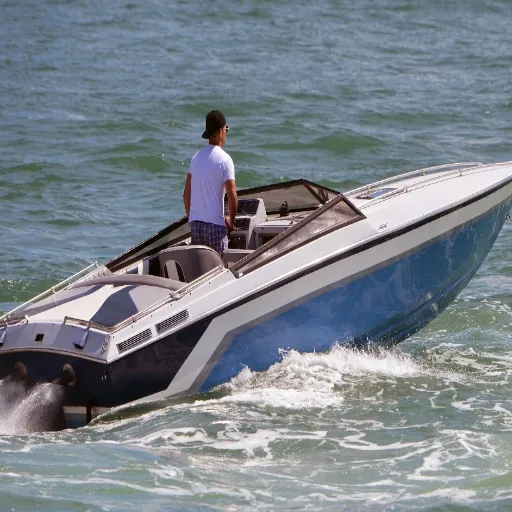
The boating community will often face that fundamental question of motor selection: to go inboard or outboard? Both have their pros and cons, and choosing one over the other might make or break someone’s boating experience, from performance to maintenance and general versatility. The guide explores the key differences between inboard and outboard motors, presenting a detailed comparison for boaters of all levels of experience to make an informed decision in 2025. The down-to-earth explanation of their main differences will allow you to focus on one or the other, considering factors such as power, maintenance, or the type of water activity that suits you best. Read on to understand the distinguishing factors between the two while learning how to make your boating a little better.
Understanding Inboard and Outboard Motors
1
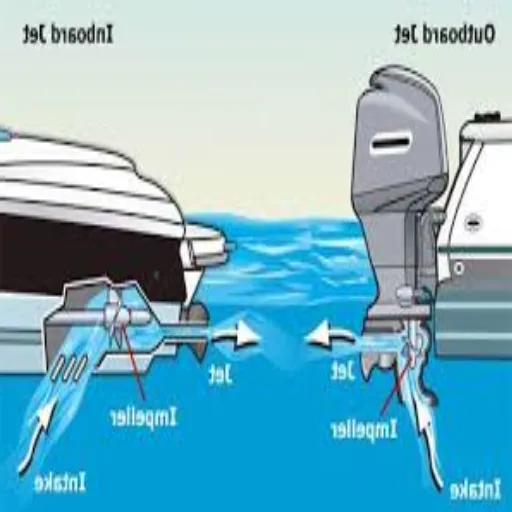
Defining Inboard Motors
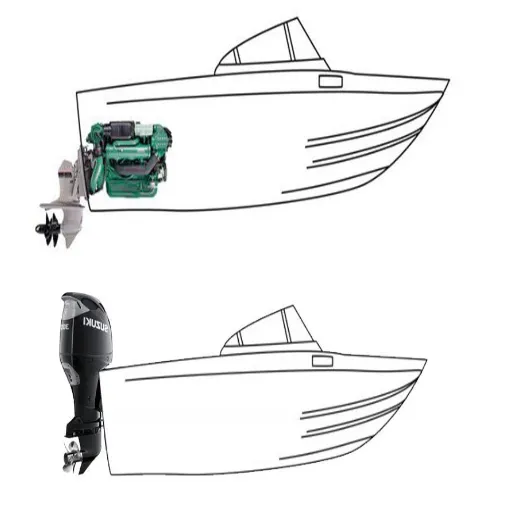
An inboard motor is installed inboard, so the boat’s hull must usually be positioned near the center, as this helps with balancing and efficiency. These engines connect directly to a drive shaft that goes down into the boat and turns a propeller. Considered extremely durable, inboard motors provide a smoother ride, making them often used for water sports, fishing, and extended cruising.
✓ Key Advantages of Inboard Motors
- Quieter operation due to sound insulation around the motor
- Better aesthetics with all machinery hidden away
- Better fuel efficiency and more consistent engine performance
- Excellent for heavier vessels or adverse water conditions
- Provides smoother ride quality
⚠ Considerations & Trade-offs
- Require more maintenance
- Demand higher initial investment
- Fixed position makes turning and maneuvering more difficult
- May require additional devices like bow or stern thrusters
- More complex installation process
But for the serious bona fide boater or someone seeking a high-performance engine for a specific application, inboard motors lend reliability and class, staying true to their reputation.
2
Explaining Outboard Motors
An outboard motor is a complete unit consisting of an engine, gearcase, and propeller, mounted to the transom of a boat and used for propulsion. Owing to their general purpose and ease of use, outboard engines are favored by both recreational and commercial boaters. Their portability and simple installation make them good choices, especially for smaller vessels or those requiring frequent maintenance or engine replacement.
🚀 Modern Outboard Advancements
Modern outboard motors have witnessed advancements in technology, including improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and lower noise pollution. These motors can be had with the horsepower needed to meet the requirements of anything from a small fishing boat to a large powerboat.
This made the systems an easy commission to bring in options like electric starts, power tilt, and power steering. Besides offering excellent maneuvering characteristics, the outboard engine allows for full steering of the boat. This arrangement provides excellent control, particularly in tight spaces while docking or in shallow water. Despite their exposure to various elements, recent material and construction improvements have increased their lifespan and corrosion resistance. Practicality and adaptability in various water bodies will always keep outboard engines relevant.
Sterndrive Engine Overview
In some instances, sterndrives are also known as inboard/outboard engines. These engines combine the advantages typical of inboard power with the versatility of the outboard drive systems. The engine, or power unit, resides inside the boat hull, with the sterndrive situated outside, giving it a cosmetically clean look and that of efficient operation. From a stability standpoint, sterndrive systems score very high and are much sought after in recreational applications such as water skiing or wakeboarding.
🔧 Sterndrive System Benefits
- Enhanced power and torque compared to outboard motors
- Quieter running with less vibration
- Better fuel efficiency
- Improved corrosion-resistant materials
- Advanced electronic controls
- Additional trim and tilt adjustments
- Available in both gas and diesel versions
Sterndrive can come in both gas and diesel versions, covering all types of boating requirements. They are notably efficient for mid-sized to larger boats, serving as an intermediate system that strengthens power, control, and comfort. In this regard, technological refinements only solidify sterndrive engines as a popular choice among boat owners who seek an equally powerful and elegantly refined experience on the water.
Key Differences Between Inboard vs Outboard
Performance and Efficiency
The choice between an inboard or outboard motor depends on performance and efficiency considerations. Inboards are well-known for their smooth performance and excellent weight distribution, which can lead to improved handling and stability in rough water. This indeed presents a fantastic alternative for passengers who value their comfort and control on an extended trip. Bigger props, on the other hand, generally yield optimal thrust with useful activities such as water skiing or wakeboarding.
| Performance Factor | Inboard Motors | Outboard Motors |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Distribution | Excellent – centered in hull | Good – weight at stern |
| Rough Water Handling | Superior stability | Good maneuverability |
| Fuel Efficiency | Consistent performance | Superior in small/mid-sized boats |
| Speed & Acceleration | Smooth, consistent power | Quick acceleration, lightweight advantage |
| Water Depth Capability | Deep water focused | Excellent shallow water operation |
Unless otherwise stated, outboards generally offer superior maintenance ease and overall efficiency. Being lightweight provides speed and high fuel efficiency, especially in small or mid-sized boats. Additionally, outboards are versatile, as they tilt and trim to operate in both shallow and deep waters. Modern improvements to both inboards and outboards, including injection systems, engine monitors, etc., have significantly diminished the performance capacity difference, rendering both sets capable of delivering the power and efficiency the user desires.
Rotor Maintenance and Repair Considerations
While maintenance is considered an advantage of an outboard engine, the outboard is mounted on external transoms. The ability to tilt this engine out of water for cleaning and inspection of worn-out machinery and replacement-related ease is indeed a boon to the harassed boater. However, inboard engines remain stowed within the hull, and sometimes necessary repair employment obliges you to go lifting this or that working to some small, clammy, narrow hole; needless work time and therefore cost are at the doorstep.
✅ Outboard Maintenance Advantages
- External mounting allows easy access
- Can tilt out of water for cleaning and inspection
- Modular design reduces maintenance costs
- Simple oil changes and spark plug replacement
- Easy upgrading or complete replacement
⚠️ Inboard Maintenance Challenges
- Located within hull – limited access
- Higher service charges due to location
- More complex maintenance procedures
- Requires specialized tools and expertise
- Longer maintenance downtime
In modern engines, monitoring systems are considered advanced to facilitate ease of maintenance. It is regarded as an advanced monitoring system, as it performs real-time diagnosis to alert boat owners of possible discrepancies, such as low oil pressure, excessive temperature, and low battery voltage, before they develop into significant problems. Preventive maintenance remains important whether it is inboard or outboard. This maintenance involves changing the oil and oil filter, replacing spark plugs, and thoroughly flushing the engine after use in saltwater to ensure smooth operation and prevent expensive repairs.
Additionally, the longevity of either type of engine depends significantly on proper upkeep. Water pump inspections, fuel line upgrades, and winterization procedures are some key considerations for boat owners in areas with colder climates. In the long run, outboards incur slightly less maintenance cost due to their modular design, while both engines benefit from a thorough maintenance log of service history to boost their resale value. Whether inboard or outboard, trust a proper maintenance program to give an engine the reliability and performance it deserves on the water.
Cost Analysis: Inboard vs Outboard
The cost implications of an inboard versus an outboard engine include the purchase price, installation, fuel efficiency, and maintenance costs over time. Usually, outboards reach a lower initial purchase price than their inboard counterparts. Nonetheless, this differs greatly depending on the size and brand of the engines. Installing outboard motors typically proves more straightforward and less expensive than installing inboard engines, especially in the case of smaller boats, where the compact design allows for an easier mounting procedure.
| Cost Factor | Inboard | Outboard | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Purchase Price | Higher | Lower | Outboard |
| Installation Cost | More expensive | Less expensive | Outboard |
| Fuel Efficiency | Consistent | Superior (modern models) | Outboard |
| Maintenance Cost | Higher service charges | Lower due to accessibility | Outboard |
| Longevity | Longer if maintained | Good with proper care | Inboard |
| Resale Value | Niche market appeal | Higher demand | Outboard |
Another important cost factor is fuel consumption. Concerning fuel economy, modern outboard engines, notably those equipped with fuel injection in contrast to older inboards, generally can perform better. But some recent inboards also have technologies to enhance fuel efficiency, thereby narrowing that gap. For the daily boaters, the cumulative fuel consumption difference can be quite large in terms of expense.
Maintenance aspects also contribute toward distinguishing things. An outboard motor, being located outside the craft, is relatively simple to maintain. It’s pretty easy to change the oil or replace the spark plug. Additionally, upgrading or replacing them completely remains relatively easy. On the other hand, an inboard engine might command a higher service charge due to its location within the boat, but it is usually much sturdier and may offer prolonged life if properly maintained.
Resale value certainly adds another feather in the price-cap analysis. In terms of popularity and ease of servicing, boats with outboard motors may see higher demand in resales, whereas boats with inboard motors may appeal to niche audiences, particularly those enthusiasts involved in water sports or those seeking a relatively quiet ride.
The ultimate choice between inboard and outboard engines is often a balance between the initial installation price, maintenance expenses, and charter-related applications. If one understands the value trade-offs, enabling them to weigh their position critically on these fronts, they can make an ideal choice that fits their application style and long-term service needs, rather than just opting for a cheap or costly installation price.
Choosing the Right Motor for Your Boat Type
Choosing Inboard Engines: Best Practices
In the process of buying an inboard engine, the selection must remain in tune with the demands of your boat type and his activities. Begin by checking the size and weight of your vessel, as the smallest of these can significantly impact the engine’s performance. Due to their higher horsepower, larger boats can operate more efficiently and maneuver, whereas smaller ones require an engine that runs quietly and smoothly.
- Assess Boat Size and Weight: Larger boats benefit from higher horsepower inboards for efficient operation and maneuverability, while smaller vessels need engines that prioritize quiet, smooth operation.
- Consider Fuel Type: Gasoline-powered engines are usually cheaper initially, while diesel engines, although more expensive, stretch your fuel money further and provide more power for an extended period, making them well-suited to long-distance boating or commercial use.
- Evaluate Maintenance Requirements: Most modern inboard engines with electronic-controlled systems make diagnosing and maintaining easier, thus reducing downtime.
- Review Propeller Shaft System: Consider the treatment of the propeller shaft system and engine placement, as it significantly impacts boat handling and stability.
- Prioritize Comfort Features: If the engines come with all the technical innovations for reducing vibrations and noise, then the comforts on board would be much appreciated, especially for pleasure cruises or long trips.
- Check Environmental Standards: Opt for engines whose pollution and fuel consumption standards are standardized by the industry. Many newer models comply with environmental regulations, ensuring low carbon footprints without sacrificing maximum output.
Technically speaking, they meet the criteria for an inboard engine, offering good operational efficiency and sustainability, which enables boat owners to achieve high performance tailored to their specific water activities.
Choosing Outboard Motors for Specific Boat Categories
Outboard motors run vital errands on trucks to enhance their functionality, improve the boat’s performance, and improve the boat’s efficiency in various categories. The choice of a motor almost entirely depends on the kind of boat, the intended use, and the expected performance.
| Boat Category | Recommended HP Range | Key Features | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Fishing Boats | 2.5 – 20 HP | Lightweight, portable | Fishing, easy transport |
| Pontoon Boats | 50 – 150 HP | Smooth ride, multiple passengers | Leisure, family outings |
| Large Powerboats | 200+ HP | High power, twin/triple configurations | Offshore fishing, long distances |
| Offshore Vessels | 200+ HP (Multiple Units) | Backup power, high capacity | Commercial, turbulent waters |
Lightweight outboard motors with horsepower ranging from 2.5 to 20 are suitable for small fishing boats. The right motor will provide just enough propulsion while also being easy to carry around. Medium-range outboard motors, ranging from 50 to 150 HP, are ideal for pontoon boats, which are typically used for leisure and family outings, to provide a smooth ride with multiple passengers.
For large boats, such as powerboats or offshore fishing vessels, navigating turbulent waters and covering lengthy distances under aluminum skies requires high-powered outboards exceeding 200 HP. The two- and three-outboard power combinations have now entered the big-end realm, giving a potent duo with plenty of backup and appeal to the higher capacity vessels.
⚡ Two-Stroke vs Four-Stroke Considerations
Four-stroke outboards require further consideration from their owners, as they are significantly quieter and, therefore, consume more fuel than their two-stroke counterparts, which are more polluting. Knowing these differences helps make an informed decision that suits the vessel’s specific needs and enhances one’s boating enjoyment.
Comparing Pontoon vs Deck Boats
The pontoon and deck boats have their separate charms and benefits, depending on what type of lifestyle a person has on the water. A pontoon boat, by its layout, is just perfect for slow cruising, family outings, or social events. Its flat deck offers plenty of feet, and one, of course, can expect a very stable ride in flat waters. An advanced version of pontoon boats now offers water sports, although one might argue that speed and performance take a back seat to pleasure.
🚤 Pontoon Boats
- Excellent stability in flat water
- Maximum deck space
- Perfect for social gatherings
- Family-friendly design
- Comfortable for slow cruising
⚡ Deck Boats
- V-hull design for dynamic performance
- Higher speeds and better handling
- Excellent for watersports
- Superior agility and maneuverability
- Better performance in varied conditions
Deck boats, conversely, have hulls with a V-profile, ensuring more dynamic performance and high speeds, which is why they are often an attraction to watersports enthusiasts and those who value handling and agility. They usually also offer lots of seating and have an open layout, though at least in still water, pontoon boats are usually a bit more stable.
Factors to consider when evaluating the two are the number of passengers, space for equipment, types of water activities, and cruising speed. Pontoons are ordinarily family-friendly outings and chill cruises. If versatility ranks high on the list, performance through a series of water conditions might take top billing, putting deck boats in a strong position. By contrasting these defining traits, the boater opts for the one that fits smoothly into his/her recreational desires.
Trends in Marine Engines for 2025
Modern Technologies for Inboard and Outboard Motors
In 2025, new innovations emerged in the marine engine sector to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and performance. Perhaps the most significant advancement has been in hybrid propulsion systems, where a traditional internal combustion engine is hybridized with an electric motor. As they operate, hybrid propulsion systems enable boats to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions, thereby promoting global sustainability, while also allowing for quieter low-speed cruising.
🚀 2025 Key Technology Advances
- Hybrid Propulsion Systems: Combining traditional engines with electric motors
- Advanced Materials: Lightweight composites and alloys reducing engine weight
- Enhanced Cooling Technologies: Ensuring greater engine longevity and reliability
- Digital Connectivity: Smart systems with real-time diagnostics and remote control
- Electric Outboards: High-capacity lithium-ion batteries with extended range
The manufacture of motors using advanced materials, such as lightweight composites or alloys, is reducing engine weight. From this, the reduction translates into improved fuel efficiency, and from there, aided speed and handling that combine to offer a delightful experience to boaters. More advanced cooling technologies are also being adopted, which will ensure greater engine longevity and enhanced reliability in longer service applications across diverse water conditions.
Digital connectivity is becoming an increasingly prominent hallmark of modern inboard and outboard motors. Manufacturers are installing smart systems that can make real-time diagnoses and performance analyses, and offer remote-control functionalities, whether via a mobile or onboard interface. These innovations enable users to have detailed information about maintenance needs and efficiency metrics, thus optimizing the boating experience.
Recently, however, the focus on green considerations has fostered the growth of electric outboard motors, which have a full clientele and are becoming increasingly prevalent in areas that strictly enforce environmental regulations. Since these motors employ high-capacity lithium-ion batteries that ensure a sufficiently long range and rapid charging, they are establishing themselves as valid alternatives for both recreational and professional boaters. The ongoing development thus ensures that the marine engine continues to establish new limits in terms of performance, sustainability, and technological integration.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
With a sustainable focus, the marine engine field is shifting toward lessening environmental impacts. Today, increasingly and modernly, propulsion systems are being designed with electric and hybrid engines to lower greenhouse gas emissions triggered by traditional engines. Industry research claims electric engines contribute to a 75% reduction in carbon dioxide emissions, with no direct pollution discharge into the marine ecosystem. This is among the factors in sustaining aquatic biodiversity and minimizing water pollution.
| Sustainability Factor | Traditional Engines | Electric/Hybrid Engines | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Emissions | High | 75% reduction | Significant improvement |
| Water Pollution | Direct discharge | No direct pollution | Protects marine ecosystem |
| Noise Pollution | Moderate to high | Minimal | Reduces marine life disturbance |
| Material Usage | Standard materials | Recyclable composites | Supports circular economy |
The use of environmentally friendly materials in production processes remains critical to the sustainability programs. Furthermore, to ensure that engines serve efficiently and contribute to the circular economy, advanced composites or recyclable materials are being considered. On the other hand, various regulatory frameworks maintain incentive mechanisms for developing propulsion systems that adhere to stringent environmental criteria, which further encourage innovation.
Renewable energy infrastructure investments are also on the rise, which include solar charging stations for electric boats. These implementations accord with global climate efforts while offering options to boat owners. Hence, through these modern solutions, the marine industry is entering an era of lower carbon emissions and greener technology, where both performance and environmental consciousness are balanced.
Consumer Preferences in the Boating Industry
Consumer choices in the boating industry have veritably tended toward more sustainable and efficient options. The prioritized technologies are now those that are environmentally friendly, including electric and hybrid propulsion systems, which aim to reduce emissions while saving money in the long run. There is also an increase in demand for boats made with eco-friendly materials, such as recycled composites and components, as well as those along crystalline lines, driven by sustainability initiatives worldwide.
- Environmental Consciousness: Increased demand for electric and hybrid propulsion systems to reduce emissions and long-term costs
- Connected Technology: Modern buyers seek enhanced navigation systems, smart sensors, and mobile apps providing real-time data on fuel consumption, weather forecasts, and maintenance needs
- Customization Demand: From custom interiors to personalized layouts, consumers favor boats fitted to their specific tastes and lifestyles
- Multi-functional Design: Appeal for convertible seating or modular deck configurations offering adaptability for different uses, from leisure cruising to fishing
- Affordability and Convenience: Growing interest in subscription services or fractional ownership models allowing boat enjoyment without maintenance and storage costs
Connected technology aboard would be another notable trend among buyers. Modern buyers sought enhanced systems of navigation, smart sensors, and mobile apps, which together provided real-time data on fuel consumption, weather forecasts, and maintenance needs. All of these innovations are highly desirable largely because they improve safety, as well as convenience and efficiency, for the modern consumer.
Ultimately, affordability and convenience play a significant role in the decision to purchase a boat. There is growing interest in subscription services or fractional ownership models, which allow individuals to enjoy the benefits of boat ownership without the associated maintenance and storage costs. This points to the evolving consumer landscape, where sustainability, technology, and flexibility become the new set of expectations for the boating market.
Real-World Case Studies and Data
Success Stories with Inboard Motors
Thinking back on success stories with inboard motors, it’s just the innumerable methods whereby they have transformed the boating experience for the individual or the business. For example, a marina owner converted his entire fleet to vessels powered by modern inboard motors. With this change, he had lower operating costs on his side and less maintenance time for his staff due to the longevity and efficiency of the inboard designs. Consequently, he was able to take in more clients, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and growing the company.
📊 Marina Fleet Conversion Results
- Operating Costs: Reduced by 30% due to fuel efficiency
- Maintenance Time: Decreased staff maintenance hours
- Client Capacity: Increased due to improved efficiency
- Customer Satisfaction: Enhanced due to smoother, quieter operation
- Business Growth: Expanded operations and profitability
Easy-to-use inboard motors have caused a revolution for the private waterside crafts community. One family I know said that changing to an inboard motor design practically made all of their weekend outings perfect. The ride was smoother; the engine was dirt, quiet (considering the loud outboards), and with that came mostly quiet boat rides that did not disrupt any sort of enjoyment. Handling was marvelous. Safety was also an issue, especially for watersports; the motor being away from the back of the boat helped reduce hazards for swimmers and wakeboarders. Such practical, real-world effects are the reasons why so many in the boating populace are selecting inboard motors as a genuinely safe and future-proof option.
Outboard Motor Performance Benchmarks
When assessing performance benchmarks, an outboard motor achieves the balance of power, efficiency, and reliability necessary for various boating activities. I consider horsepower a major factor, as it determines how the motor deals with different water conditions and loads that may be imposed upon it. Additionally, I consider fuel efficiency and emission ratings, as the costs of operation and environmental sustainability are always key factors in my decision-making process. Apart from that, I believe in evaluating the top speed and acceleration, mainly for jobs such as fishing and watersports, where extra performance attributes improve the experience.
| Performance Metric | Small Outboards (2.5-20 HP) |
Medium Outboards (50-150 HP) |
Large Outboards (200+ HP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horsepower Range | 2.5 – 20 HP | 50 – 150 HP | 200+ HP |
| Fuel Efficiency | Excellent | Very Good | Good |
| Top Speed Capability | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High | High to Very High |
| Acceleration | Quick for size | Excellent | Outstanding |
| Noise Level | Low to Moderate | Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Maintenance Ease | Excellent | Very Good | Good |
Another crucial aspect in my model evaluation is durability and ease of maintenance. Since outboard motors must withstand the harsh conditions of saltwater and repeated use, I compare the models based on their corrosion resistance and serviceability. Noise levels also factor somewhat into my consideration: the quieter the engine, the more pleasant the overall experience. This is particularly true when it comes to leisure activities or wildlife observation. Additionally, I now measure performance benchmarks with outboard motors that incorporate cutting-edge technologies, such as GPS and digital controls, thereby offering convenience, accuracy, and safety on the water.
Ultimately, the performance benchmarks for an outboard motor are established to align features with realistic needs. An outboard motor almost needs to have consistent performance, regardless of maintenance issues, and power that works in harmony with efficiency to be an ideal candidate for me. Such standards ensure that every trip on the water, whether for leisure or a more serious activity, operates smoothly with minimal impact on the business and the environment.
Market Trends and Sales Data for 2025
Upon analyzing 2025 market trends and sales data, several clear indicators emerge that affect the landscape of outboard motors. Foremost, there is a growing awareness of environmental factors and the need to set stricter emission norms, which calls for greener and fuel-efficient models. Manufacturers and buyers are now focusing on sustainability. This is evident in an increasing proportion of advanced electric and hybrid outboard motor models from the installation base. This shift towards sustainability makes sense from the perspective of global green initiatives, but it also helps buyers be conscious of cost savings on long-term operational expenses.
The boating community will often face that fundamental question of motor selection: to go inboard or outboard? Both have their pros and cons, and choosing one over the other might make or break someone’s boating experience, from performance to maintenance and general versatility. The guide explores the key differences between inboard and outboard motors, presenting a detailed comparison for boaters of all levels of experience to make an informed decision in 2025. The down-to-earth explanation of their main differences will allow you to focus on one or the other, considering factors such as power, maintenance, or the type of water activity that suits you best. Read on to understand the distinguishing factors between the two while learning how to make your boating a little better.
📈 2025 Market Trends Summary
- Environmental Focus: Stricter emission norms driving demand for greener models
- Electric & Hybrid Growth: Increasing proportion of advanced propulsion systems
- Recreational Dominance: Compact and versatile motors leading sales
- High-Power Commercial: Robust sales for industrial applications
- Technology Integration: IoT-enabled controls becoming standard
On the sales side, I can observe that compact and versatile outboard motors have continued to dominate the market, especially those designed for recreational boating. The flourishing sector of recreational water sports and personal watercraft provides strong support for this category. On the other hand, high-horsepower models continue to enjoy robust sales for commercial and industrial applications, thereby catering to the specific needs of another audience. And increasingly, the technology is becoming a tie-breaker, adding to the price of precision and convenience, for example, IoT-enabled controls and smart systems.
A steady growth in sales is projected for 2025, driven by innovation and evolving consumer preferences. The viewpoint is that companies that promote their products as reliable and efficient, and meet sustainability trends, stand to do well in the competition. These dynamics emphasize that, alongside basic performance, the modern world has demands on motors that can satisfy both practical and aspirational needs. A company adopts a market program that addresses existing customers while simultaneously appealing to new customers who want to invest in innovative solutions.
Reference Sources
-
Outboard vs. Inboard: Which Motor is Right for You? – Discover Boating
Explains the ease of servicing outboard motors compared to inboard motors, along with other key differences. -
Inboard vs Outboard Motors – Key Differences, Pros, and Cons – GetMyBoat
Highlights power, efficiency, and suitability of inboard motors for larger boats versus outboard motors. -
Inboard vs. Outboard Motors: Which is Best for Your Boat? – Sportsman Boats
Discusses performance, speed, space, layout, maintenance, and fuel efficiency differences. -
Outboard vs. Inboard Outboard: Which Boat to Buy? – Hurricane Boats
Focuses on the design and functionality of inboard-outboard boats, including space and usability. - Find more info now.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
❓ What is the primary difference between inboard and outboard engines?
The primary difference between inboard and outboard engines is their location. Inboard engines are installed inside the boat, usually in the engine compartment, while the outboard engines are installed outside of the boat, typically along the boat’s transom. Depending on the location, factors such as maintenance, performance, and even the type of boat itself come into play. Inboard engines offer better stability and weight distribution, making them a better choice for larger boats. Outboard engines are always more maneuverable and easier to work with. Another advantage of inboard engines is that, with their generally lower center of gravity, they offer better performance for water sports.
⚖️ What are the advantages and disadvantages of inboard and outboard engines?
Both inboard and outboard motors pose tradeoffs. Inboard engines are typically quieter and better suited for handling larger boats, offering a choice for both recreational and fishing boats. They are more challenging to access when it comes to maintenance. Outboards, in contrast, are easier to remove for service and more versatile in shallow water situations. These types of engines can be tilted out of the water to prevent marine growth or corrosion. Inboards generally perform better in rough waters, and they are quieter compared to outboards.
🚤 Are outboard engines better for pontoon boats?
The ease of installation and maintenance makes outboards preferable for pontoon boats. Most pontoon boats make use of outboard motors because these engines may be mounted onto the transom of the boat, causing more room inside. This arrangement also facilitates navigation in shallow waters. With outboards, the horsepower can be chosen freely, thereby increasing the horsepower for various water activities on a pontoon. Larger pontoons, conversely, may be preferred with inboards for water sports, particularly for stability and weight distribution.
🛥️ How does the type of boat influence the choice of inboard or outboard motor?
When considering the type of boat, one must weigh the benefits of inboard versus outboard engines. Generally, smaller boats tend to be fitted with outboard motors, primarily due to factors such as weight and maneuverability. Outboards are therefore suitable for recreational activities and fishing. Larger vessels, such as deck boats and motor yachts, often prefer the inboard engine for its enhanced stability and power. Sports boats for watersports, such as wakeboarding and skiing, might benefit from inboard engine performance. Therefore, the hull design and purpose of the ship will lead you to the choice of the engine.
🔧 What maintenance issues should I consider with an inboard and an outboard motor?
Maintenance issues vary significantly between inboard and outboard motors. Inboard engines are typically located inside the engine compartment of the boat, making maintenance quite challenging due to limited access. It is essential to regularly check for water intrusion and ensure the water pump is functioning correctly. Outboard engines, however, are easier to maintain: they have an outside mount on the boat and can be tilted up entirely out of the water for repairs. It is essential to check for marine growth and corrosion for outboards, especially in saltwater environments. Each motor type has its unique characteristics that must be addressed in terms of maintenance to ensure it lasts and performs optimally.
🏄 Can I use a watersports device with an outboard motor?
Yes, they’re truly good for water sports, and many recreational boats come for that purpose. The outboard motors accentuate acceleration and fast maneuverability for wakeboarding, skiing, or tubing. Another upside is that they can be trimmed up from water within minutes, thus preventing marine growth and corrosion-related problems, especially when in saltwater. However, when large sizes come into play, inboard engines for water sports may take the lead due to their weight and stability. Ultimately, the deciding factor would be the type of boat and the desired watersport activities.