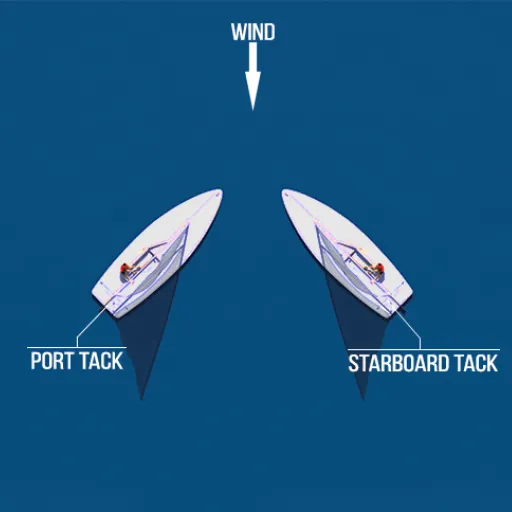
The industry is rapidly changing, and as we approach 2025, the debate between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines has never been more relevant. When discussing boating consumers and industry players, we cannot afford to neglect the basic features that distinguish these engines, as this will likely set a precedent for future trends and practices in boating, particularly in terms of environmental impact, efficiency, and performance. Could the 2-stroke make a comeback through the latest innovations? Or will the efficiency and durability of the 4-stroke keep it on top? We will now focus on how one engine type or the other affects performance, technology, and ecology, providing a comprehensive picture of the future trends facing the boating industry. These insights will help you make informed decisions and stay ahead in the evolving maritime landscape.
Understanding Outboard Engine Types
2
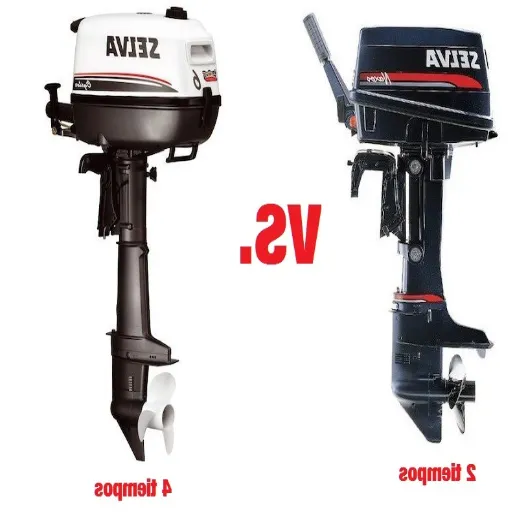
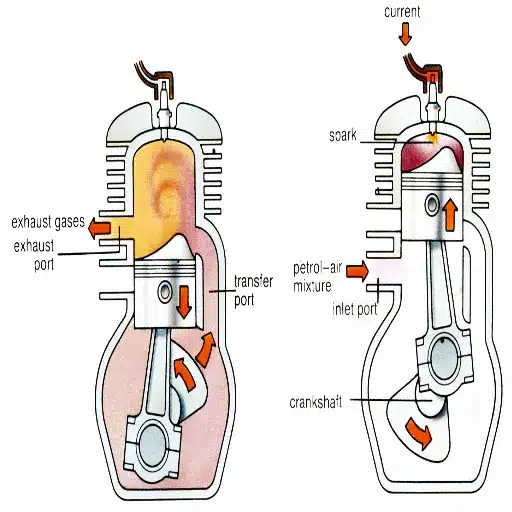
What is a 2 Stroke Outboard Motor?
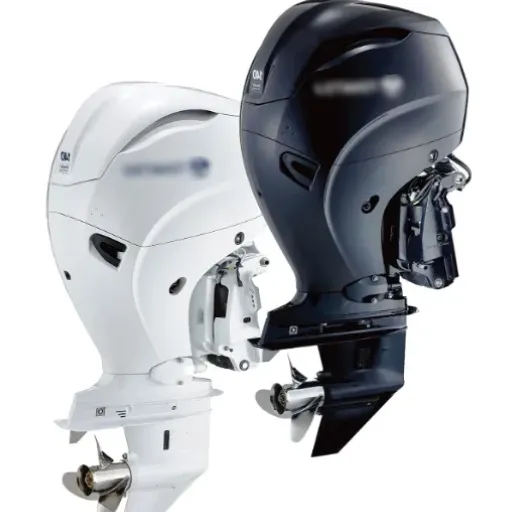
A 2-stroke outboard motor is an internal combustion engine designed to power boats, completing one power stroke in only two strokes of the piston. Such an operation in two strokes instead of four strokes, as does the four-stroke engine, reduces the complexity of the machinery and finally produces higher power-to-weight ratios. Thus, the 2-stroke motors are lightweight and compact and are used for speed in smaller to midsize boats where agility and performance are essential.
Recent years have witnessed significant development in modern 2-stroke outboard motors. Until recently, concern regarding the ecological impact of these motors was offset by DFI technologies that improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. For example, a technology-forward 2-stroke engine model uses up to 50% less fuel than past two-stroke models while meeting strict emissions standards. Additionally, this type of engine is characterized by very responsive acceleration and can reach upwards of 6,000 RPMs quickly, making them preferable when water skiing or fishing in a tight corner.
While maintaining them is easy due to their fewer moving parts, one consideration is that they tend to consume more oil, a trade-off that is sometimes weighed when choosing between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke. Nonetheless, the upshot remains their cost-effective versatility, which is attractive to any boater looking for power and performance in compact packaging.
4
What is a 4 Stroke Outboard Motor?
The four-stroke outboard motor is one type of marine engine designed to achieve quieter operation, greater fuel efficiency, and lower emissions compared to the 2-stroke engine. Unlike 2-stroke engines, 4-stroke engines operate through a more complex process, where the work cycle is divided into four stages: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. In this way, the fuel burns more smoothly and cleanly, thereby improving fuel economy and reducing emissions.
Due to their reliability and durability, the older model often finds its way into recreational use, being used for fishing and water sports. Additionally, the quieter nature of these motors makes for an enjoyable experience, where loud splashing is not welcome. Although 4-stroke outboard engines tend to be heavier and cost more due to their initial outlay, they often prove to be the economical choice in the long run because of their durability and reduced oil consumption.
As technology improves, performance continues to enhance, providing boaters with the perfect blend of power, efficiency, and sustainability.
Key Differences Between 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke Engines
| Aspect | 2-Stroke Engines | 4-Stroke Engines |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Higher power-to-weight ratio, power stroke every revolution | More even power delivery, power stroke every second revolution |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to fuel loss during combustion | More efficient with controlled combustion process |
| Maintenance | Simpler with fewer moving parts but higher wear | Complex design but built for durability |
| Weight | Lightweight and portable | Heavier due to more components |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions, mixing oil with fuel | Lower emissions, separate oil reservoir |
| Cost | Lower initial cost but higher operating expenses | Higher upfront but better long-term value |
Key Takeaway
From the very start, users have the opportunity to make an informed choice, depending on their specific needs, which include considering aspects such as power, efficiency, cost, and the environment.
Performance Analysis of 2 Stroke vs 4 Stroke Outboards
Torque and Power Ratings Comparison
Comparing torque and power ratings between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines is a crucial consideration in evaluating their performance delivery characteristics. Torque is generally exerted from a 2-stroke engine at low revolutions. This will accelerate the engine very quickly and significantly increase the application’s thrust. It becomes favorable for water sports or some kind of immediate power requirement when negotiating rough conditions.
Conversely, power is meant to be delivered steadily and perpetually by a 4-stroke type over a relatively wider range of RPMs. Accordingly, under low RPM conditions, a 4-stroke engine may not exhibit the power output of a 2-stroke engine, but it generally excels in power storage and fuel efficiency during extended runs. To illustrate, a mid-range 4-stroke outboard engine typically retains its horsepower better at cruising speed. It thus favors fishing or other leisure pursuits.
Recent experience has shown a further narrowing of the distinction between the two types of power plants with modern technology. Recently, 2-stroke engines have adopted direct fuel injection (DFI) systems to reduce fuel consumption and improve emissions performance, while 4-stroke engines, in the meantime, continue to evolve towards lighter-weight construction and increased horsepower output. Linear to that consideration is the use-by-use basis: quick bursts of power or long, smooth-running operation.
Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Fuel efficiency and environmental impact are the chief considerations when comparing 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. Traditionally, four-stroke engines have been considered more fuel-efficient due to their more controlled combustion process. Generally, they burn less fuel over time, making them suitable for prolonged use and applications where fuel efficiency is crucial. However, in the case of 2-stroke engines, although they excel at providing high power-to-weight ratios, many have faced issues of incomplete combustion and fuel waste.
Recently, technological advances brought drastic changes in this scenario. While new 2-stroke engines with direct fuel-injection technology had filled the fuel-efficiency gap, they also markedly reduce the emissions of unburned fuel. Such improvements make it an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers. 4-stroke engines, on the other hand, still operate in lean burn mode, where they can work with fuel mixtures that ensure full efficiency without compromising actual power output.
As an environmental consequence, emission concerns constitute the deciding factor here. Manufacturers have been compelled to prioritize clean engine technology. By design, along with advancements in catalytic converters, current 4-stroke engines emit less pollution. Similarly, the new generation of 2-stroke engines has made advances in achieving low emission levels by reducing fuel loss and improving combustion mechanisms.
The final decision between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines depends on the specific use and priorities. The 4-strokes, if efficiency and reduced pollution are put aside in the long run, are an acceptable option in modern designs. Conversely, for power users requiring high output in small appliances with minimal compromise on fuel efficiency, the latest 2-stroke engines now stand as very competitive and environmentally responsible.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Engine Type
2-Stroke Maintenance
- More frequent service intervals
- Constant fuel and oil mixing required
- Shorter spark plug life
- Regular exhaust system cleaning
- Frequent inspections for wear and tear
4-Stroke Maintenance
- Oil changes every 50-100 hours
- Separate lubrication system
- Valve adjustment and timing inspections
- Periodic air and fuel filter checks
- Cooling system maintenance
Modern Enhancement: Both engines receive modern-day enhancements: synthetic lubricants are applied to increase longevity and minimize residue formation. Users must adhere to the manufacturer’s described service intervals and use the correct-grade lubricants and fuels. Properly applied, this approach will lengthen and enhance the life of their engines. While express maintenance for each may be distinct, generally, consistent care and timely maintenance keep each of the 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines in top working condition.
Boating Trends Influenced by Engine Type in 2025
Growing Popularity of 4-Stroke Outboard Motors
Their rising popularity in 2025 can be attributed to advancements in efficiency, environmental considerations, and engineering. They are known to be more fuel-efficient than 2-stroke engines, allowing users to travel long distances on comparatively less fuel, which aligns with growing concerns about sustainability. Manufacturers, on their part, have continued to work on redesigns that reduce emissions, making the 4-stroke an immaculate option whose performance standards have not been compromised due to stringent regulations.
And they say 4-stroke motors are among the best for durability and reliability. Their quieter operation promotes a better experience, especially for recreational boaters who have to maintain the serene environment. The improvements in technology have enabled modern 4-stroke engines to compete with increased horsepower while retaining a streamlined size and reduced weight, making them suitable for a wider range of vessels.
A shift toward these engines trends steadily in the commercial and recreational sectors. Industry reports indicate that a significant percentage of new boat purchases favor 4-stroke outboard motors, which consumers perceive as offering a fair balance of performance and cost over time. Another factor promoting this trend was the maintenance advantage, characterized by long service intervals and the availability of modern diagnostic tools that minimize downtime and the cost of maintenance. These factors give a strong pull for further dominance of the marine engine market by 4-stroke outboard motors.
Technological Innovations in Outboard Engines
Key Innovation Areas
Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)
Precision fuel delivery for improved efficiency and reduced emissions
Noise & Vibration Control
Advanced materials for quieter, more comfortable operation
Digital Integration
GPS navigation, smart controls, and performance monitoring
Hybrid & Electric Options
Sustainable alternatives for environmentally conscious boaters
Technological advancements in the outboard engine market emphasize performance, efficiency, and environmental objectives. Outboard motor manufacturers are now incorporating electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems to achieve fuel efficiency while optimizing engine response. This technology delivers fuel with precision, resulting in smooth operation, reduced noise, and lower emissions.
On the other hand, advanced noise and vibration control technologies have enhanced the user experience by reducing engine noise and improving comfort during operation. Innovations in lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys and composite parts, enable more compact and portable design solutions without compromising durability and power output.
Furthermore, digital integration has enhanced the user experience with features such as GPS navigation, smart throttle controls, and engine performance monitors in the newly introduced outboard motors. These systems provide real-time data and diagnostics, enabling users to be the most efficient and cost-effective in the maintenance process.
Moreover, hybrid and electric outboards are gaining popularity due to the growing trend of environmental consciousness. These models reduce noise pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, paving the way for sustainable marine technology. With enormous investment in research and development, the outboard engine industry continues to set the industry standards in producing more innovative, cleaner, and more powerful solutions to accommodate ever-changing consumer demands.
Consumer Preferences and Market Demand
Consumer tastes in the outboard engine market are evolving in step with the merger of performance and conscience. Consumers, by and large, are looking for engines that offer better fuel economy, reliability, and quieter operation while boating, emphasizing what presents the best boating experience. Requests for lightweight and easy-to-use designs support both novice and experienced boat users, ensuring simplicity in operation and maintenance.
Recent data suggest that there has been an increase in demand for hybrid and electric outboard engines, driven by the global sustainability movement. In the eyes of environmentally-conscious boaters, these greener alternatives help reduce the carbon footprint without compromising power and performance. The increasing adoption of these models is also facilitated by supportive regulations and incentives in various regions, encouraging the transition to greener technology.
In addition, recreational boating is experiencing an increasing demand for integrated digital features, such as GPS compatibility, smart controls, and real-time diagnostics. This aligns with the trend of consumers seeking modern, connected boating solutions. Manufacturers are integrating new technologies that enhance usability and enable engines to achieve top-level performance.
The overall outboard engine market exhibits strong momentum at the intersection of innovative performance, sustainable design, and shifting consumer preferences for more innovative, more efficient products. These developments indicate a continually adapting market that responds to the dynamic needs of its end-users.
Choosing the Right Outboard Motor for Your Boat
Factors to Consider before Buying a Motor
- 1
Horsepower Rating
The rating for horsepower will be paramount, matching it to the boat’s size and the load it can bear. If the motor is rated too low, the boat will slow down, lose balance, and reduce fuel efficiency, potentially endangering the driver’s life. Conversely, too much horsepower will become a burden for the operator, and a significant amount of extra power will be wasted.
- 2
Fuel Consumption
In modern times, outboard motors have increasingly been configured in terms of power versus fuel consumption. Look for models that incorporate advanced technologies, such as fuel injection, which optimize fuel usage and minimize emissions. Also consider whether you want a two-stroke or a four-stroke; generally, a four-stroke will provide a quieter, smoother ride, departing from the two-stroke, which is lighter and hence faster in acceleration.
- 3
Technology Features
Features would include keeping an eye on any new technology created to ease the user experience; digital controls assist in this aspect by making it easy to navigate and maneuver through the usage. Keep an eye on noise levels too, especially if you plan to use your boat for fishing or other relaxing activities where a bit of quiet would enhance the experience.
- 4
Maintenance Requirements
The practical aspect that comes into play is maintenance. Having motor systems with self-diagnostic abilities acts in favor of labor-saving maintenance and alerts you to problems that could escalate into expensive repairs if left unaddressed. Additionally, it is essential to assess the availability of service centers and spare parts in your region beforehand, so that there is no unnecessary delay in case of repairs.
- 5
Environmental Compliance
The environmental compliance regulations of today should never be disregarded either. Many models must comply with more stringent emissions limits set forth by environmental authorities. Those with lower emissions are judged so by the power of good; under certain local laws, you might even obtain some incentives or tax breaks.
Final Consideration: The combination of these factors will ensure that you have a motor that delivers the highest possible performance while being attuned to current efficiency and sustainability trends, thereby enhancing your boating experience and satisfaction in the long run.
2 Stroke vs 4 Stroke: Which is Right for You?
Choose 2-Stroke If You Need:
- ⚡ Quick acceleration and high power
- 🪶 Lightweight and portable design
- 💰 Lower initial purchase cost
- 🔧 Simpler maintenance requirements
- 🏁 Performance for water sports
Choose 4-Stroke If You Need:
- ⛽ Better fuel efficiency
- 🔇 Quieter operation
- 🌱 Lower emissions
- ⚙️ Long-term durability
- 🎣 Smooth cruising and fishing
Having considered the decision between the 2-stroke and 4-stroke motor, understanding their differences will help you make a truly informed decision about what fits your needs and criteria. 2-stroke engines are generally lighter and more compact, as well as having higher power-to-weight ratios. This makes them ideal for smaller boats or for situations needing fast maneuvers. They also require less maintenance, since they have fewer moving parts; yet, they are louder and less fuel-efficient than the 4-stroke types.
4-stroke motors, in contrast, are known to be more fuel-efficient, operate more smoothly, and meet today’s pollution standards. They consequently will take up more weight; thus, they are apt for applications where the boat has to perform steadily over long durations, such as fishing or cruising. Moreover, being quieter and less vibratory will contribute to making the boating experience more comfortable.
Choosing the motor is purely a question of priority: if one looks at performance and portability, a 2-stroke will perhaps be his preferred choice. Yet, the 4-stroke motor will be deemed more reliable, environmentally conscious, and much more efficient. These factors, paired with your boating requirements, will make sure you buy the motor that suits your preferences and use.
Future Outlook for Outboard Motors
Predicted Developments in Engine Technology
Since we are talking about shaping futures for engine technology in outboard motors, there are some exciting developments I would love to see. An expanding array of electric and hybrid engines may be one of the most prominent future scenarios. This technology addresses an increasing concern for a clean environment, with attributes including being quieter, producing less smoke, and requiring fewer maintenance works than traditional combustion systems. Hence, in my view, this global trend advocating sustainability and electrifying transportation will likely make outboard motors more environmentally friendly and efficient than ever before.
Another trend that I envision evolving alongside this is the integration of innovative technologies within the engine design. Features such as advanced diagnostics, real-time performance monitoring, and app-based controls could absolutely enhance the user experience. These technologies may provide boaters with a deeper understanding of their engines’ status and, at the same time, make maintenance tasks easier through operational alerts and optimizations. In my vision, the level of technology would be such that engine management would almost run itself, leaving the user with little interference in deriving optimal performance from an engine.
Ultimately, I perceive improvements in lightweight materials and aerodynamic designs evolving into further advances in engine efficiency and portability. Advanced materials, such as carbon composites, may enhance durability while maintaining a low weight, making motors lighter and more powerful. With these developments around the corner, I envision the future of outboard motors as one defined by performance, sustainability, and user-centric features that cater to the evolving needs of the boating fraternity.
Regulatory Influence on Two-Stroke and Four-Stroke Engines
The primary purpose of regulating agencies is to shape the design, performance, and environmental impact of 2- and 4-stroke engines. As emission standards became stricter, these grades were considered to have a more profound effect on the development of 2-stroke engines, given that these engines have traditionally been considered to emit higher levels of unburned fuel and pollution. To meet the required regulations, manufacturers have been utilizing technologies such as direct fuel injection, which provides for reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions. While such improvements have paved the way for a viable case for cleaner 2-stroke engines, the flip side is that such technologies have also raised production costs, making them less affordable for mass adoption. However, they are still attractive for some applications due to their excellent power-to-weight ratio and lightweight characteristics, such as personal watercraft or smaller boats.
In contrast, the inherently cleaner and more fuel-efficient 4-stroke engine is favored by regulations that emphasize sustainability. These engines emit fewer pollutants because their combustion process is more efficient, and therefore, they meet current environmental standards more effectively. Meeting the ever-changing set of regulations has spurred the evolution of catalytic converters and advanced fuel management systems, enabling a higher level of performance and environmental sustainability. Still, regulation has been a factor in the rise in complexity and cost of these engines, making them an impediment to some users.
From my perspective, these regulations have a positive impact on the industry by compelling manufacturers to adopt sustainable technologies. Obviously, they might cause problems in terms of costs and design, but with the greater good being provided in terms of a lesser environmental impact, greater fuel efficiency, and performance-enhanced engines, the benefits outweigh the drawbacks. For us, users, adhering to these regulations means continuing to enjoy these engines with a smaller environmental footprint. It is surely good for the growth of the industry and our Earth as well.
Trends in the Market to Watch Out For in the Coming Years
Key Market Trends
Green Technologies
Sustainable practices and eco-friendly innovations
AI & Automation
Smart systems and automated processes
Personalization
User-centric and customized experiences
Considering the trends ahead in the market, I observe a significant surge in the adoption of green technologies and sustainable practices across industries. Consumers and businesses alike emphasize the importance of being environmentally friendly, driving innovation in processes and products. For me, this translates to being aware of advancements such as renewable energy options, carbon-neutral production, and eco-friendly materials, as all will become essential parts of being competitive and satisfying both regulatory and client expectations.
Fast-paced integration of AI and automation is another trend. AI tools are helping companies transform their operations, from optimizing manufacturing processes to enhancing customer experiences. I am particularly active in advocating for increased efficiency and streamlined decision-making through these technologies, which can provide agile, data-driven strategies to counter new market demands. Yet, the need to balance innovation with ethics and transparency cannot be overemphasized.
The acceleration in the demand for personalization and user-centric design is a phenomenon even I cannot ignore. When consumers are asking for individualized experiences, companies prioritize grasping and foreseeing these singular needs through data and analytics. To me, this highlights the importance of using insights to design highly targeted offerings that foster loyalty and long-term engagement. These trends bring with them complex challenges, but they can also be advantageous opportunities in which to excel in the changing market landscape.
Reference Sources
-
2-Stroke vs. 4-Stroke Outboard Motors (Pros and Cons) – UTI: Discusses the differences in weight, size, and performance between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines.
-
Comparison Between 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke Outboard Engines – Reliable Marine Service: Highlights cost, weight, and power differences to help boaters choose the right engine.
-
Differences Between 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Outboard Motors – RJ Nautical: Explores affordability, maintenance, and performance aspects of both engine types.
-
Best Outboard Motors 2025 – Buyer’s Guide for Every Boater – GetBoat: Focuses on 2025 outboard motor trends, including fuel economy and weight reduction.
-
Hot Trends in Boating in Early 2025 – Salvage Marine: Covers emerging boating trends like sustainability, alternative power sources, and advanced technology.
- Click here to read more.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary notion that differentiates a 2-stroke outboard motor from a 4-stroke one?
The primary difference between 2-stroke and 4-stroke outboard motors lies in their operating cycle. A 2-stroke engine produces one power cycle with two strokes of the piston, whereas a 4-stroke engine produces one cycle with four strokes of the piston. This gives the 2-stroke outboards more power for their weight; hence, the 2-stroke outboards are lighter and much more powerful in comparison to 4-stroke engines. But, generally speaking, a 4-stroke engine is quieter, more fuel-efficient, and has less pollution. Thus, the selection depends on the boat and its intended purpose.
Are 2-stroke outboard motors more fuel-efficient than their 4-stroke counterparts?
Typically, 4-stroke outboards give better mileage over 2-stroke outboards. The two-stroke engines are lighter and possess higher horsepower, but they burn more fuel and produce higher emissions in the atmosphere due to their combustion process. The modern 4-stroke engine utilizes fuel injection technology, which enables it to burn fuel more completely, resulting in improved fuel economy. Therefore, based on fuel efficiency and lower emissions, a 4-stroke engine would be the best choice.
How do maintenance requirements differ for the two outboard motors, the 2-stroke and the 4-stroke?
Maintenance is very different—according to a lot of literature—between 2- and 4-stroke kinds of outboards. Two-stroke motors typically require more frequent oil changes and also necessitate the inconvenience of mixing oil with fuel. On the contrary, the lubrication system in 4-stroke outboards ensures that the oil is changed less frequently, resulting in lower maintenance. This advantage makes 4-stroke outboards hassle-free. Yet, the simpler 2-stroke design might be advantageous in some situations.
Which outboard motor is right for my boat type?
The difference between 2-stroke and 4-stroke outboard motors depends much on one’s boat type and use. A 2-stroke outboard is suited for a smaller, lighter boat that requires quick acceleration and power. A 4-stroke engine would better suit one who wants efficiency in fuel consumption, quiet operation, and lower emissions. Brands that offer these services in various models to suit different boat types include Yamaha, Suzuki, and Evinrude.
Do 2-stroke outboards produce more torque than 4-stroke counterparts?
2-stroke outboards have the capacity to produce larger torque when run at higher RPMs. This primarily results from the design of a 2-stroke engine, which enables more rapid power production during the power cycle. However, 4-stroke engines will deliver smoother torque and use less fuel at lower RPMs. The choice could be based on the type of performance you are looking for or how you want to operate the boat.
How do 2-stroke outboard engines compare to 4-strokes in terms of emissions?
Emissions are a very important factor when choosing between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke outboard engine. Older 2-stroke motors have been known to produce more emissions due to their design, which mixes oil and fuel. Conversely, the newer 4-stroke outboards have all been environmentally friendly, generally featuring fuel injection systems that significantly reduce emissions. If you are concerned about environmental impact, the responsible choice would be to consider purchasing a 4-stroke outboard motor.